1Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
2National Research Foundation, Singapore
3University of Cambridge, United Kingdom
Mixed-phase TiO2 nanoparticles (10-20 nm) composed of rutile, anatase and srilankite phases are prepared through a one-step flame synthesis method. The phase composition of TiO2 nanoparticles can be easily tuned by changing the flame conditions such as the gas flow rates of the fuel, oxygen and argon carrier. The optimized anatase/rutile/srilankite TiO2 sample with as low as 0.1 wt% of Pt co-catalyst exhibits remarkable photocatalytic H2 generation rate of 21.9 mmol h-1 g-1 and an apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) of 39.4% at 360 nm, higher than those of anatase/rutile or anatase TiO2. The less studied srilankite phase is first time investigated for photocatalytic H2 generation. It is revealed that the relatively low content of srilankite phase in TiO2 could efficiently promote charge separation and transportation. It is remarkable that compared to the commercial P25 TiO2, the flame made TiO2 significantly improves Pt reduction and dispersion owing to the oxygen vacancies and surface defects. The optimized TiO2 sample with surface defects facilitates the deposition of ultra-small Pt nanoclusters of around 0.63 nm and stabilizes the low valence state of Pt0, leading to efficient utilization of noble metal and remarkable enhancement of H2 generation rate.
Biography:
Shuyang Wu is a current PhD student in School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. His main research interest lies in the area of flame synthesized metal oxide for the applications in energy and environment, including photocatalytic hydrogen generation, CO2 reduction and volatile organic compounds degradation.
Petra University, Jordan
The aim of our investigation that we are looking for reducing resistance tendency, the current interest in the development of new antimicrobial agent is due to increasing bacterial resistance to antibiotic therapy and newly pathogens.
Benzimidazole (starting material) derivatives play an important role in medicinal field with so many pharmacological activities, benzimidazole shows their antibacterial activity by inhabiting the bacterial nucleic acid and proteins synthesis due to structure similarity with purine, our target based on benzimidazole derivatives.
It is possible to design a wide range of potential microbial inhibitors by replacing the hydrogen at various position of benzimidazole ring with different functional groups.
The most derivatives with substituents at the 2-mercabto group like phthalic anhydride and the resulted carboxyl group were converted to various alkyl, acyl group.
We are interest in modifying 2-mercabtobenzimidazole to generate more effective class of compound and may be resistant to microbial.
Experimental:
Chemicals:
1. 2-mercabtobenzimidazole
2. propylgyl bromide
3. alcohol
4. potassium bicarbonate
5. phthalic anhydride
Instrument:
1. IR
2. 2- H-NMR
3. 3- ELEMENTAL ANALYSIS
4. 4- MARVINʼS SKETCH
5. 5- CHEM SKETCH
6. C-NMR
Chemical procedure:
1. Design and synthesis new compounds and mechanism of their actions.
2. Evaluation its antimicrobial activity.
3. Interpretation of these results.
4. Conclusion
Anadolu University, Turkey
Paraoxonase (PON) is a mammalian lactonase that especially exists in the liver and HDL-bound enzyme. PON1 is synthesized in the liver and released from here into the blood. Decrease of PON1 activities may related with some metabolic or genetic disorders such as diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, chronic renal failure, age-related macular degeneration and hyperthyroidism.
In the present study, in vitro effects of Equisetum arvense, Origanum vulgare, Achillea millefolium, Artemisia absinthium and Hypericum perforatum on human serum PON1 were investigated. For this reason, PON1 was purified with 1928.6 EU x protein-1 specific activity from human serum. The purity of PON1 was checked by SDS PAGE. Subunit molecular weight of the enzyme was determined as 43 kDa. Subsequently, water and alcohol extractions of the plants were prepared. Moreover, chemical contents of these extracts were carried out by LS-MS/MS study. The extracts were tested at various concentrations and increased in vitro hPON1 activity. The results indicated that both water and alcohol extracts of Hypericum perforatum had the highest activity effect. However, water extract of Equisetum arvense showed lowest activity compared with other extracts. In addition, the molecular docking analyses of compounds in the plant contents were carried out to understand the estimated binding interactions on the active site of the PON1 enzyme.
Biography:
Şükrü Beydemir, Ph.D, Professor of Biochemistry in the Biochemistry Department at Faculty of Pharmacy at the University of Anadolu, Turkey. Beydemirʼs group have interest in purification and characterization of various enzymes, drug-enzyme interactions and designing enzyme inhibitors. Prof. Beydemir and his group have recently worked on especially carbonic anhydrase I and II isozymes, paroxonase, aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase enzymes. Prof. Beydemir has 114 manuscripts and a lot of presentation on these areas.
Anadolu University, Turkey
Carbonic anhydrases (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) are metalloenzymes containing a zinc ion in the active site. The enzyme is responsible for the transformation of CO2 HCO3- in the respiratory. They are play a significant role in a variety of pathological and physiological effects containing fluid balance, neurological disorders, osteoporosis, bone resorption, pH regulation, carboxylation reactions, glaucoma, calcification, cancer, tumorigenicity. During the literature research, it has been encountered that sulfanilnamide compounds display CA inhibitor activity. Thus, sulfanilamide derivatives have been extensively studied to develop n ovel CA inhibitor.
Prompted from CA inhibitory potency of sulphonamide derivatives, in the present study ten new sulfonilamide derivatives (1-10) were prepared. IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and HRMS spectroscopic analyses were used for structure elucidations of target compounds. Purified carbonic anhydrases (hCAI and II) isozymes from human erythrocytes with yield of 31% were used to determine the in vitro inhibitor potentials of the compounds. Compound 6 displayed the best esterase activity against both hCA1 and hCAII. However, the highest hydratase activity against CA1 and hCAII isoenzymes was recorded for compounds 8. In addition, MTT assay was performed to determine cytotoxic potential of compounds 6 and 8. Both compounds did not display any cytotoxicity against NIH/3T3 cell line. All these results indicated once more that sulfanilnamide derivatives have a good potency to inhibit CAs and supported the previous studies.
Biography:
Şükrü Beydemir, Ph.D, Professor of Biochemistry in the Biochemistry Department at Faculty of Pharmacy at the University of Anadolu, Turkey. Beydemirʼs group have interest in purification and characterization of various enzymes, drug-enzyme interactions and designing enzyme inhibitors. Prof. Beydemir and his group have recently worked on especially carbonic anhydrase I and II isozymes, paroxonase, aldose reductase and sorbitol dehydrogenase enzymes. Prof. Beydemir has 114 manuscripts and a lot of presentation on these areas.
1Department of Organic Chemistry and Technology, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary
2Institute of Enzymology, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Hungary
The synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates is an evergreen field in organophosphorus chemistry due to the bioactivity of the products. The most common synthetic route towards α-hydroxyphosphonates is the addition of dialkylphosphite to an oxo compound (Pudovik reaction). This reaction is usually carried out under solvent-free conditions in the literature. However, during the work-up procedure, a considerable amount of organic solvents is used. We have elaborated a new, green procedure for the synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates by reducing the use of organic solvents to the minimum [1]. The α-hydroxyphosphonates so obtained were subjected to phosphorylations and phosphinoylations to afford α-phosphoryloxyphosphonates and α-phosphinoyloxyphosphonates as new compounds (Scheme 1) [2].
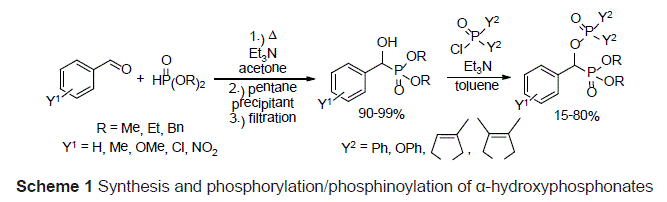
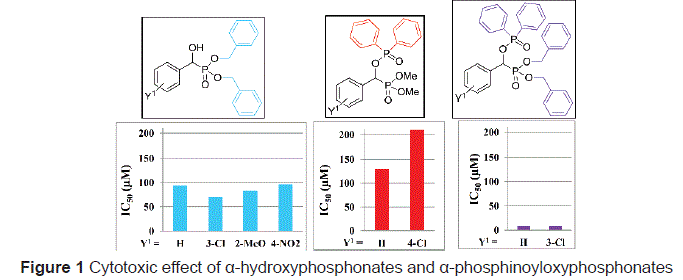
α-Hydroxyphosphonates and α-phosphoryloxyphosphonates obtained by us were screened against Mes-Sa human sarcoma cell line as potential cytotoxic agents. Among α-hydroxyphosphonates, dibenzyl esters were found as hits [3], while among a-phosphinoyloxyphosphonates phenyl-containing derivatives showed moderate cytotoxic activity. The next idea was the combination of the scaffolds of the hit molecules. The reaction of dibenzyl 1-hydroxy-1-phenylmethyl-phosphonates with diphenyl phosphinic chloride resulted in more effective compounds with IC50 values of 8-9 μM (Figure 1). These results are promising for further investigation of these compounds as potential cytotoxic agents.
[1] Keglevich G., Rádai Z., Kiss N. Z.Green Process. Synth.2017,6, 197-201.
[2] Rádai, Z.; Hodula, V.; Kiss, N. Z.; Kóti, J.; Keglevich, G. Mendeleev Commun.2019, 29, in press.
[3] Rádai Z., Szeles P., Kiss N.Z., Hegedus L., Windt T., Nagy V., Keglevich G. Heteroatom Chem.2018,e21436.
Z. Rádai was supported by the ÚNKP-18-3-IV-BME-265 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities.
Biography:
Zita Rádai graduated from the Budapest University of Technology and Economics in 2016 as a pharmaceutical engineer. She has been a PhD student since 2016 at the Department of Organic Chemistry and Technology at the same university, under the supervision of Professor Dr. György Keglevich. Her main fields of interest cover organophosphorus chemistry, microwave-assisted chemistry and green synthesis. She is the author or co-author of about twenty research or review articles and book chapters.
University of Mosul, Iraq
New series of complexes of general formula [ML (AA)(H2O)]; where M=Co, Ni and Cu ions; LH2=o-xanthatosalicyldazine and AA=amino acids (glycine, alanine, valine, leucine and phenylalanine) were synthesized. The complexes were synthesized from the direct reaction of the metal (II) chloride with a mixture of the ligand (LH2) and the amino acids (AA) in a molar ratio of 1:1:1 respectively. These complexes were characterized by several physical methods such as melting points, molar conductance and elemental analysis (M), magnetic moments as well spectral such as infrared and electronic spectral measurements. These studies revealed that the Ligand (LH2) was behaved as a tridentate, divalent and coordinated to the metal (II) ion through both the oxygen atoms of xanthato groups and one nitrogen atom of azine moiety. As well, the existence of one aqua molecule with the nitrogen and the oxygen atoms of the amino acids to give the most probable octahedral geometry around each metal ion in each complex. The elemental analysis (M) as well the infrared spectra proved the presence of an aqua molecule inside the coordination sphere. Their molar conductance measurements revealed the non-electrolytic behavior of the synthesized complexes.
1Atatürk University, Turkey
2King Saud University, Saudi Arabia
In this study, a series of novel bromophenol derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their acetylcholinesterase and α-glycosidase enzymes inhibition properties and antioxidant activity. Diarylmethanones were synthesized and their bromination was carried out. During bromination, some compounds gave new bromophenols via regioselective O-demethylation. Demethylation of brominated diarylmethanones was also performed with BBr3 to give novel bromophenols. In addition, we examines the antioxidant capacity of novel bromophenol derivatives using several in vitro bioanalytical methodologies such as 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTSŸ+) and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl free radical (DPPHŸ) radical scavenging activity, Fe3+ and Cu2+ reducing activities and ferrous (Fe2+) ions chelating activities. Also, novel bromophenols and methoxylated bromophenols derivatives were tested against acetylcholinesterase and α-glycosidase, which associated with some metabolic diseases. The novel bromophenols showed Ki values in range of 8.94±0.73-59.45±14.97 nM against AChE and 4.31±1.93-44.14±2.19 nM against α-glycosidase enzyme.
Biography:
Prof. Dr. İlhami Gülcin obtained a doctorate (Ph.D.) in Chemistry from the Ataturk University of Erzurum, Turkey. He is the member of Turkish Academy of Sciences (TÜBA). He has experience in the research of enzyme purification, enzyme inhibition, antioxidant activity and biological activities. He has also published more than 300 scientific publications, which covered by SCI. His manuscripts have more than 15000 citations.
South Refineries Company, Iraq
Hierarchical porous carbon (HPC) monolithic with 3D network has received considerable attention due to their potentially technological application as candidates for electrochemical energy storage devices such as capacitors, lithium ion batteries, solar cells, sorbent for toxic gas separation and greenhouse gas capture for their well-defined pore dimensions and topologies. Synthetic polymer based hierarchical nanostructured carbons are particularly attractive for their consistent pore dimensions which can be adjustable on long length scales, so that diffusibility of guest species could be improved through its unique hierarchical pores. N-doped HPC monoliths exhibit multifaceted features such as tunable textural properties, excellent thermal and chemical stability, which are remarkable physicochemical properties that are answerable for micro/nanostructured porous carbons perfect candidates for emerging substrates in nanotechnology science.
A two-step synthetic method has been developed to achieve functionalized nanoporous carbons via cross-linked polymer precursors, which are prepared by Friedel-Craft alkylation and pyrolysis. Nitrogen-doping proves to be an effective method for reinforcing the CO2 adsorption capacity of carbon-based adsorbents, although it remains a great challenge to reach a fit doping level of nitrogen (N) and a high porosity in a porous carbon simultaneously. Herein, a facile method that enables the fabrication of ordered microporous nitrogen-doped porous carbon monolith with a content of 4.6 wt% N, which employs poly (H-BINAM) as precursor. Through chemical activation, high microporosity is generated and gives birth to a monolithic structured porous nitrogen-doped carbon. This material exhibits a remarkable CO2 adsorption capacity (6.74 mmol g-1 at 273 K and 4.27 mmol g-1 at 298 K under 1 bar) and an extraordinarily excellent CO2/N2 selectivity (153), which is calculated from the single-component adsorption isotherms based on Henryʼs Law. This value exceeds the CO2/N2 selectivity of thus mentioned for carbon-based adsorbents including diverse nitrogen doped ones, whose attributes are largely associated with the unusually high N-content as well as the partial graphitic framework.
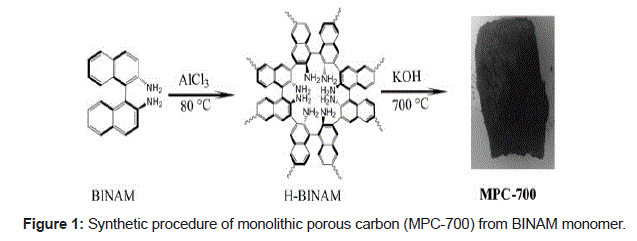
Biography:
Dr. Alabadi Akram has the expertise in chemistry of microporous polymers and their applications in petroleum fields, lubricant oils properties and enhanced oil recovery where he contributed over 7 articles. Currently, he is holding the chemist in lube oil department at South Refineries Company, Basra, Iraq. In over 17 years, Dr. Alabadi Akram also has external lecture at university of Basra.
Mosul University, Iraq
The aim of this study was designed to determine the effect of hypertension on the level of lipid fractions and percentage of fatty acids in serum. The study included (50) patients with hypertension, blood was taken after (10-12) hour fasting. The age of patients was between (60-80) year. Blood samples from (50) normal subject with the same age were collected as control. The patients samples collection were from the medical word. A number of biochemical parameters were measured using enzymatic kits methods also the analysis and the measurement of percentage of fatty acids in fatty component of serum (cholesterol ester, phospholipids, triglyceride) separated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) followed by transmethylation of fatty acids and measurement of fatty acids percentage using Capillary Gas Chromatography (CGC). The result of this study showed that there is a significant differences in the level of studied biochemical parameter and fatty acids percentage in hypertension patients compared with the control group. The results of this study also showed that a significant increase in level of (TG) in serum of hypertension patients. The result showed that a significant increase in percentage of (PUFA) in (PL) part.