Peer review is a process wherein the scientific research work of an author is evaluated for its validity, authenticity, relevance, and significance by his/her peers, that is, experts from the author's own field. This process holds considerable importance for the publication of scientific articles because peer review is used by the journalreviewers to decide whether a particular submission is suitable for publication in a particular journal.
Experts selected for a peer review include those who have worked in that specific field of research and are therefore well versed in the subject area. Owing to their experience and the fact that they are updated on the current research topics being explored in their field, these experts are able to accurately judge the suitability of a candidate manuscript. In addition, they are able to provide useful and valuable feedback to the authors that could help improve the manuscript and increase the chances of acceptance by a journal.
Types of Peer Review
Different publishers use different types of peer-review processes as per publisher policy. In order to understand the type of review process that your target journal follows, you need to visit their home page or contact the editorial office of the journal.
Considerable research effort, patience, and diligence are involved in conducting a study, preparing a manuscript, and finally submitting it to a carefully curated journal. Therefore, it is important that journals provide a transparent peer-review process wherein the authors are communicated about the type of review that will be used for their manuscript. Some journals even provide information about the identity of the reviewers who have evaluated the manuscript, their credentials, and their comments about the research work.
The four commonly used types of peer review that are currently being used by journals are highlighted below:
1. Open review
The open review is essentially the most transparent type of peer review. Under this system, the journal discloses the identity of the reviewer and the author to each other.
Advantage
This lets the author know about the expert who is in charge of evaluating the manuscript and gives the reviewer information about the author whose work he/she is reviewing. Such a system allows a great amount of transparency and promotes trust.
Disadvantages
There is a high chance of bias under this system on the part of the reviewer. Under this model, the reviewers' assessment may be influenced by factors like politeness, professional courtesy, and personal relationship with the author if the reviewer and author are already acquainted with each other. However, this completely depends on the personal integrity and objective evaluation ability of the review expert.
On the other hand, the author may use the information about the reviewer to attempt influencing him/her in the author's favor.
2. Single-blind peer review
When a manuscript undergoes single-blind peer review, the reviewer is aware of the author's identity; however, reviewer information is withheld from the author. This is believed to be the most conventional type of peer review process and has been used most frequently for scientific publication.
Advantage
The advantage of this system is that reviewer anonymity prevents the author from influencing the reviewer in his/her favor.
Disadvantages
Knowledge of the author's identity and security about their own anonymity may lead the reviewers to delay the publication in order to push their own similar studies or be unduly critical of the author's work.
3. Double-blind peer review
The double-blind peer-review system involves blinding of both the author and reviewer information. Thus, neither the author nor the reviewer is aware of the other's identity.
Advantages
This system eliminates bias on the part of the reviewer. Since the review expert is unaware of author information, such as name, age, sex, religion, professional standing, residential location, country of origin, and institutional affiliation, there is no risk of bias owing to these factors. The evaluation is thus based purely on the merit of the written work.
The author cannot influence the reviewer since he/she is unaware of the reviewer's identity.
Disadvantage
Although this system ensures considerable author and reviewer anonymity, in certain cases, reviewers are able to identify the author based on the subject area, research topic, and writing style. It is very challenging to ensure double-blind peer review because of practical considerations and the fact that the research community is close-knit and interconnected.
4. Triple-blind peer review
This model takes the double-blind review process a step further. Similar to that in the double-blind peer-review system, the author is blinded to reviewer information. Further, author information is hidden from both the reviewer and the journaleditor. In order to ensure such a high degree of blinding, the articles are submitted in an anonymous manner and the entire process of submission to publication is tailored to support the anonymity.
Challenges
Such a degree of anonymity requires substantial planning and effort, and in spite of all precautions, it is possible for the reviewer to identify the authorbased on writing style, subject area, and study design.
Benefits of Peer Review
Most researchers agree that the peer-review system is the only method of regulating scientific publications and ensuring the dissemination of high-quality research. Here are some of the main advantages of the peer-review process and how it can be effectively used to improve a manuscript:
1) Objective feedback
A good peer review provides the author with objective feedback on the validity, relevance, and significance of the manuscript. The author is able to understand the reviewer's objective perception about the work that can help improve the manuscript presentation and add more data or analyses to increase the effectiveness and/or impact of the findings.
2) Technical accuracy
With an in-depth analysis of the manuscript, the reviewer is able to give focused feedback on the use of technical terms, commonly used terminology in the field, as well asstatistical tests and wordings. Any procedural errors can be picked up and rectified at this point to ensure that the final, published version is free from technical mistakes.
3) Scope to improve
A review from an expert can help an author understand the nuances of scientific writing and grow as a writer by incorporating the feedback in future write ups. As a direct result of the review, the author has the chance to use the feedback to improve the manuscript and make it more suitable for scientific publication.
4) Pre-publication quality check
The peer-review process works in the favor of the author because it gives him/her the opportunity of having the manuscript thoroughly evaluated by a field expert. In addition, during the review process, the reviewers are able toconduct a quality check in terms of language, grammar, and spelling.This increases the chances of the manuscript of being accepted for publication and being received well by the readership.
5) Authenticity and plagiarism check
A reviewer is able to analyze and provide insightful feedback on the study design, methodology, equipment or software used for the study, as well as the statistical tests employed to bring out correlations and other meaningful results from the collected data. In addition, an astute reviewer can determine whether the manuscript reflects original work and whether there are sections that appear plagiarized. By flagging such instances, the reviewer helps identify cases of intentional or accidental plagiarism and ensure that the journal publishes certifiably original, relevant, and accurate scientific work.
Madridge Publishers: Peer Review Process
As one of the leading publishers of reputed scientific journals, Madridge Publishers follow a fair peer-review process for each submission to ensure that the work published in each journal reflects authentic, novel, and relevant research for our vast readership.
Madridge publishers follow a double-blind peer-review process where neither the author nor the reviewer is aware of the other's identity. As mentioned previously, this type of peer review is very effective in ensuring reviewer and author anonymity. This ensures a fair, unbiased review and discourages any unethical action on part of the author to influence the reviewer. Such peer-review process is crucial for ensuring the publication of authentic, relevant, valuable, and novel research work that advances the field. As a by-product, this type of fair publication processes encourages well-versed, efficient, and competent researchers to keep giving their best to aid progress and development in the field of research.
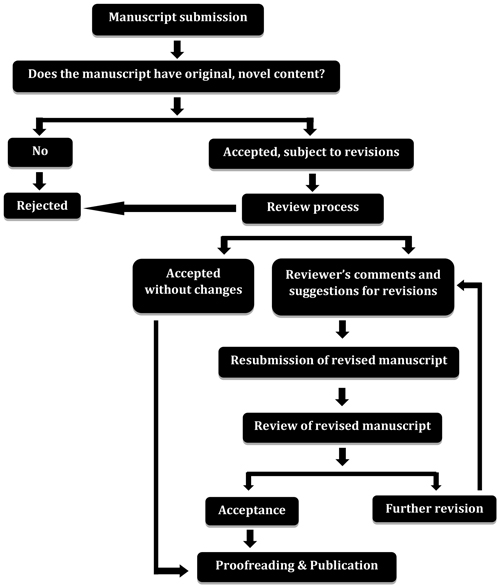
The peer-review process can be explained graphically as follows. This flowchart represents a typical peer-review process that is used by most journals for screening the submitted manuscripts.