Pharmaceutical Technology Laboratory, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Solid lipid micro particles (SLM) are lipid microscale drug reservoirs. SLM couldprotect drugs against degradation, control release and enhance oral absorption. All of these properties would allow the SLM to be used for the manufacture of lipid matrix tablets.
SLM were prepared by hot emulsion using stearyl alcohol (53%), Tween® 80 (8.0 %), Span ® 60 (5.0 %) andibuprofen (IBP) (40.0 %) as model drug.The particles were purified by freeze-drying.
The microscopy study shows two SLM populations,(spherical and acicular shape). The IBP drug payload was 98.13 + 0.52% (n=3). The angle of repose (26.73o+1.15o, n= 3), bulk density (0.2129 + 0.0034 g/mL, n=3) and tapped density (0.2384 + 0.0139 g/mL, n=3) were determinated as described at USP 39. Carr index (10.48 + 3.8 %, n=3) and Hausner index (1.12 + 0.05, n=3) were calculated considering density values.
Despite SLMʼs irregular shape, the values of CI, HI and AR indicate good flow properties, so for the preparation of the lipid matrix tablets, Cellactose® 80 as diluent (49%) and magnesium stearate as lubricant (1%) were used. The lipid matrix tablets (400mg, 12mm) were prepared applying a compression force of 500kg/cm3 during 5 seconds. The obtained tablets shows a glossy and homogeneous surface and a tablet breaking force of 6.2 + 0.36 Kp (n=5).
Finally, a dissolution test was carried on considering the pharmacopoeialconditions indicated for IBP (n= 3). Results show a controlled release with a 50.58 + 10.87% IBP free at 6 hours.
Biography:
Dr. Llera is a time part-time professor at the Faculty of Chemistry of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico (UNAM) at Pharmacy department since 2011. She studied her BSc, MCs and her PhD in Pharmaceutical Sciences at UNAM. Her main research areas are the development of nanoscale systems for drug delivery release and the design and theevaluation of new strategies to increase the bioavailability of lipophilic drugs. Her doctoral thesis work has received the poster award at APGI 3rd Conference Innovation in Drug Delivery, Advances in Local Drug Delivery (Pisa, Italia. September 2013). She has supervised eigthbachelors thesis.
Department of Mechanical and Energy Engineering, National Chiayi University, Taiwan
Flex-on-Film (FOF) packages consisting of PI flex with fine-pitch Cu circuits and ITO-coated PET films are bonded using Anisotropic Conductive Film (ACF). The electrical resistance of the packages is then evaluated under sequential static bending cycles. During the bonding process, the conductive particles in the ACF resin deform and fracture under the effects of the compression force and play a key role in determining the initial electrical conductivity of the package. The cyclic compression / tension stress produced in the subsequent bending tests prompts a propagation of the cracks in the conductive particles, and thus degrades the electrical performance of the package. In particular, the electrical resistance increases with an increasing number of bending cycles. Microscopic observations show that the higher electrical resistance is the result of a smaller overall contact area between the conductive ACF particles and the Cu electrode / ITO film due to fatigue crumbling of the particles.
Keywords: Flex-On-Film, Anisotropic Conductive Film; Conductive Particle; Microscopic; Static Bending Cycles.
Biography:
Dr. Chao-Ming Lin received the M.S. degree and Ph.D. degree from the National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan, in 1993 and 1999, respectively, and both in mechanical engineering. He is currently with the Department of Mechanical and Energy Engineering, National Chiayi University, Taiwan, as a Professor with research interests in IC packaging, injection molding processing, electrically conductive adhesive/films, nanotechnology, MEMS, and polymer packaging composites. He had some publications in the areas of electronic packaging, nanotechnology, micro fluidics and polymer processing including more than 60 journal papers, more than 60 conference papers, more than 30 technical reports, and 4 patents.
1Department of Chemistry, Lorestan University, Iran
2Freie University of Berlin, Germany
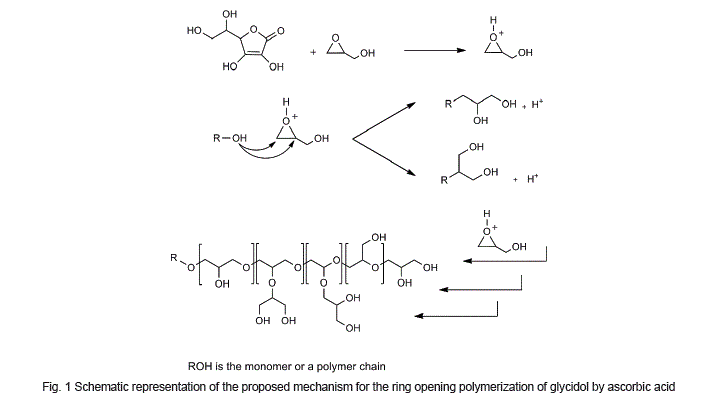
In this work, low molecular weight hyperbranched polyglycerols (LMPGs) are synthesized in bulk using ascorbic acid as an activator. Different molar ratios of glycidol and ascorbic acid were mixed and stirred at ambient conditions and LMPGs with different molecular weights, degree of branching and relative abundance of the structural units were obtained. According to spectroscopy data, ascorbic acid was not incorporated in the structure of polymer and plays the role of activating agent in the polymerization process. In this synthetic protocol, any other chemical reagent and organic solvents were not used. Therefore, products are free of toxic impurities and suitable for the future biomedical applications.
German University in Cairo, Egypt
Spacecrafts orbiting the earth is subject to plasma environment consists of charged particles. These particles hit the spacecraft external surface and deposit charges leading to discharges and arcing which alter the thermal and electrical properties of material.
Several numerical codes aiming at simulating spacecraft plasma interactions have been developed over the world. They aim at investigating the plasma dynamics, current emission/collection on spacecraft and spacecraft charging.
This work will focus on studying the structure and characteristics of anodic coating for different samples of aluminum alloys used in space applications. Modeling and simulation of these samples under space plasma conditions will be investigated using the Spacecraft Plasma Interaction Software (SPIS) code.
1LMM, Laboratory of Magnetic Materials, Algeria
2LPCMA, Laboratory physico-chemistry of advanced materials, Algeria
The purpose of this study is to exploit structural, electronic, magnetic and thermodynamic properties of the full Heusler Ag2CrGa compound using the method of calculation of linear Muffin-tin-orbital potential (FP-LMTO) in the L21 phase with the local approximations density (LDA), local spin density and the local spin (LSDA)density coupled(LSDA-couplé). The calculation made on the structural properties such as modulus, pressure derivatives and electronic properties have enabled us to deduce the nature of this alloy which proved a metal. While the calculated magnetic properties has enabled us to evaluate the magnetic moment of the test compound Ag2CrGa and the magnetic moments of each constituent element of the latter. The calculated thermodynamic properties are apparent change in modulus, heat capacity and the Debye temperature [from 0 to 1600 °C].
Biography:
Belasri Amina student in 2nd year doctorate “PhD student” she was major of promos for 5 years of her study in specialty physical of materials. She did an internship for 1 month in the malizia in the field of nanotubes, participated in a lot of conferences in many countries like morocco and tunisia.
American University of Ras Al Khaimah, UAE
In recent years, solar energy has become an alternative power supply as it is considered as a clean source of energy of great importance. Several researches and efforts have been focused on the photovoltaic (PV) systems efficiency improvement. This paper deals with an intelligent technique for theefficiency improvement and optimization of the PV control performances. A PV system topology incorporating maximum power point tracking controller (MPPT) is studied in this paper. To achieve this goal a special interest was focused fuzzy logic controller (FLC) that also was compared to the well-known P&O algorithm. This paper presents a detailed study of the MPPT regulatorin order to insure a high system performance which can be selected for practical implementation issue. A simulation work dealing with MPPT controller, a DC/DC Boost converter feeding a load is achieved. Significant extracted results are given to prove the validity of the proposed overall PV system control scheme.
Biography:
Dr. Maissa Farhat is currently an Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical, Electronics, and Communications Engineering at the American University of Ras Al Khaimah (AURAK). She Received the Ph. D. degree in control engineering automatic and robotic from the University of the Basque Country, Spain and in electrical and computer engineering from the University of Gabes, Tunisia in 2015. Received the M.Sc degree in automatic and intelligent techniques from National School of Engineering of Gabes, Tunisia in 2011. Her research interests include power electronics, converters control and renewable.